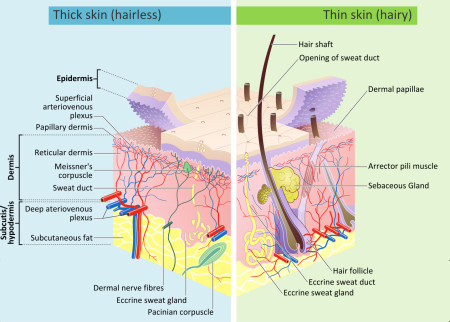
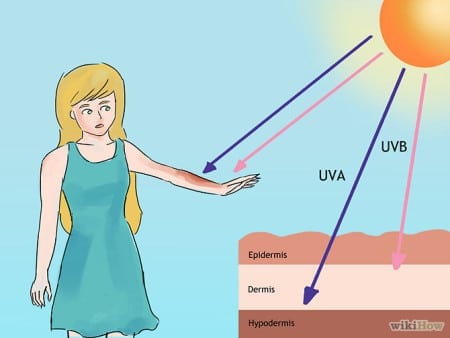
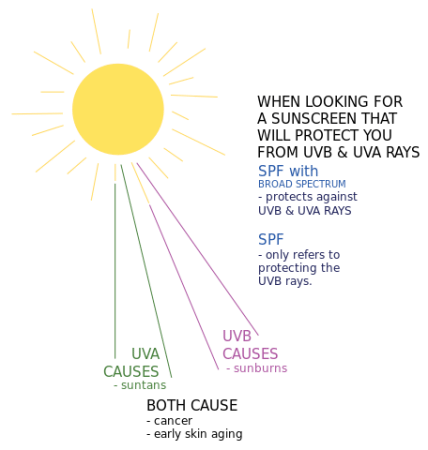
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, either from the sun or tanning beds, is a leading cause of skin cancer. For the majority of people, exposure to UV radiation comes mainly from sunlight.
With the classification of UV radiation as a human carcinogen by the World Health Organization, it is important to understand how exposure to skin damaging rays increases skin cancer risk and what you can do to minimize that risk.