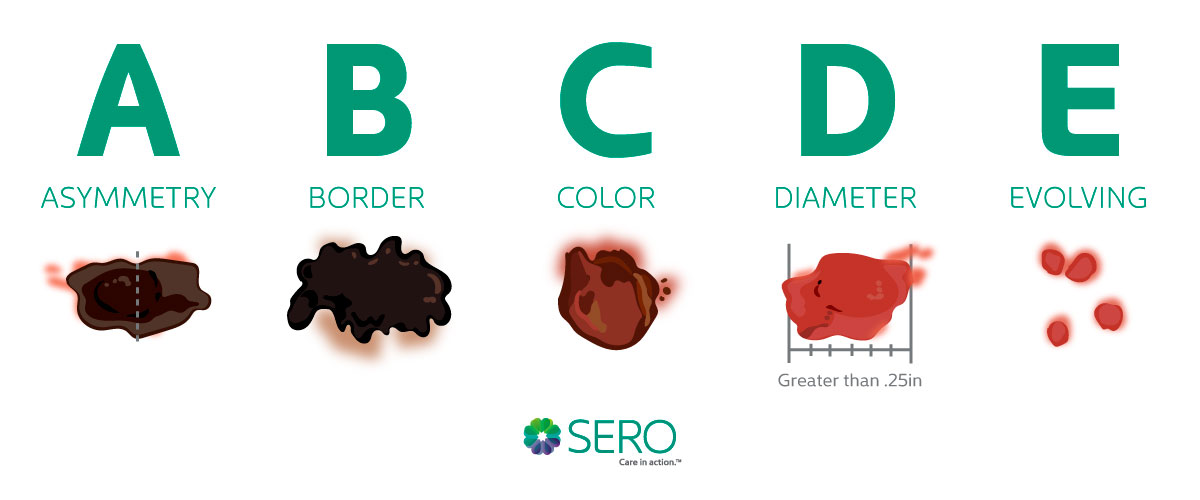
Cancer forms when cells divide out of control.
When these cells divide without any checks or balances, they can start to crowd out vital organs and release substances that can create an imbalance in the body’s regulatory system. Almost every possible cell line in the body is prone to cancer.
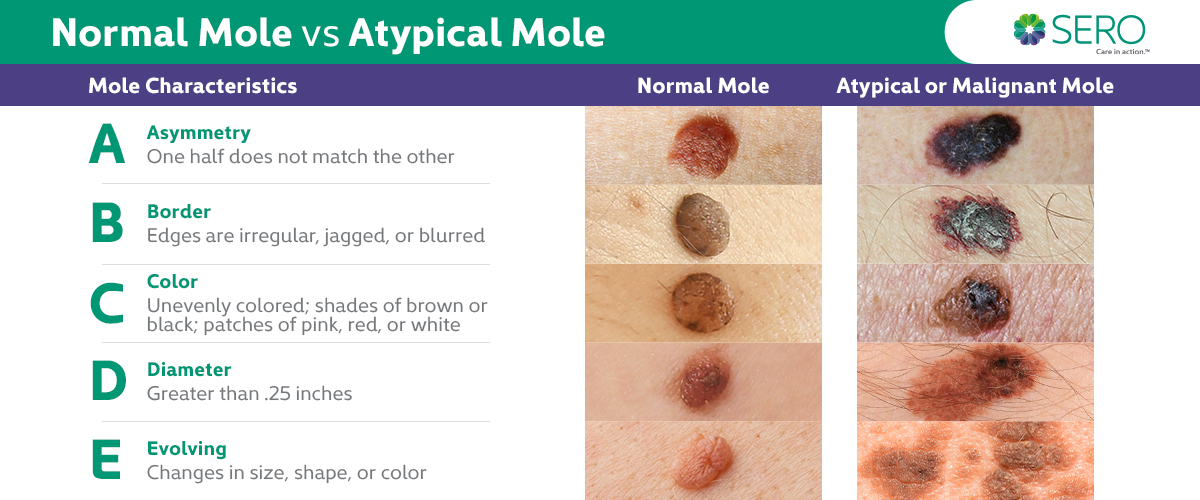
The longer people live, the more opportunities there are for something to go wrong. If an error occurs during cell division, cancer can result. One of the most common types of cancer is skin cancer.